Understanding RCM in Healthcare
RCM, or revenue cycle management, is a financial framework that enables healthcare practices to get paid for providing medical services. It is colloquially referred to as medical billing due to its complete reliance on billing and coding work. Nonetheless, it is a complete cycle that starts with the patient registration or scheduling and ends with the payment collection and posting.
RCM is a vital component of healthcare financial operations. It is a streamlined way how medical facilities get paid for their services. And it is regulated by major bodies like CMS, AMA, and HIPAA.
Steps Involved in RCM Medical Billing
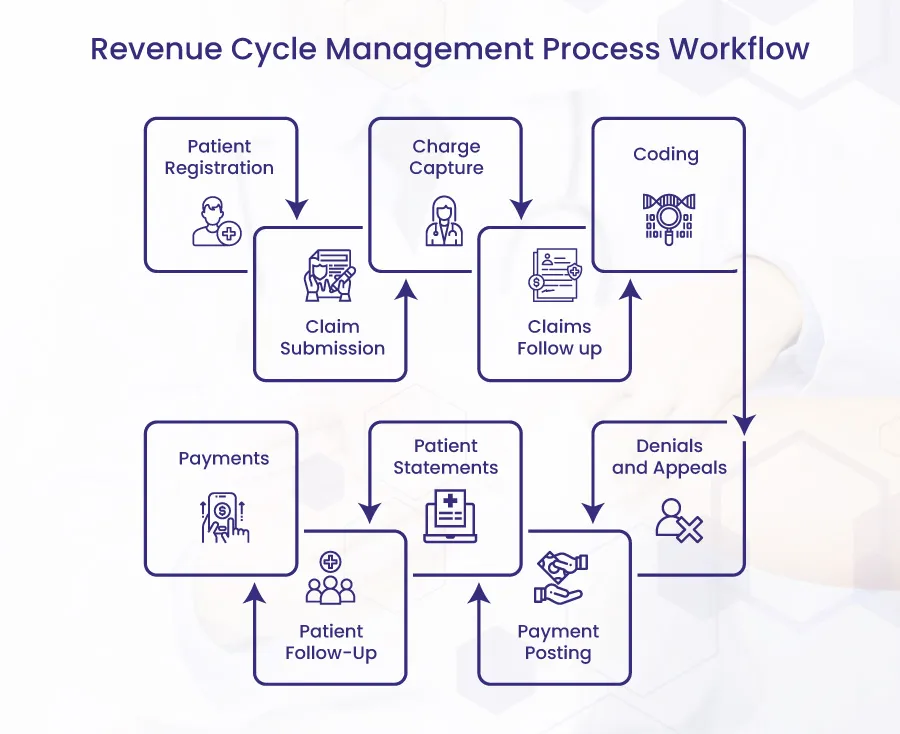
RCM fundamentally involves the following steps:
Patient Pre-Registration
It is the first step of RCM and involves collecting fundamental patient information like demographic details, contact information, and scheduling preferences. It also involves verifying their insurance eligibility to avoid any payment difficulties later on.
Insurance Verification
This step involves determining and confirming a patient’s insurance coverage and benefits. It also includes checking whether the healthcare facility has billed rendered services correctly. Down the road, insurance verification also helps estimate the patient’s responsibility.
Patient Registration
Patient registration advances the process of information collection. It involves gathering crucial patient details like medical history and patient consent. This information is then entered into the patient management system to advance the RCM process.
Charge Capture
This step involves recording and documenting all the billable services provided to the patient. The billing team must ensure that they have covered all the charges. This helps prepare precise claims.
Claim Submission
Claim submission refers to compiling and submitting the medical claim to the insurance company. It involves a number of steps before the billing team hits the send button. The major step is the allocation of the latest ICD-10 and CPT codes to the services rendered. Other important steps include insurance policy re-checking and claim scrubbing to eliminate any errors that may lead to a denial or rejection.
Claim Adjudication
Claim adjudication is a step at the payer’s end as they analyze and process the submitted claim. They examine the claim for its accuracy and compliance with the insurance policy. Then, they decide whether to proceed with the full or partial payment or deny the claim entirely. The job of the healthcare providers at this stage is to ensure they have adhered to all the steps above.
Payment Posting
During this step, the healthcare revenue team updates the patient accounts with the payments received from the payers or patients. It is one of the final checks to ensure that the payment received matches the amount billed. It is a vital process for maintaining accurate financial records.
Denial Management
In case of a denial, the RCM team works to identify, analyze, and rectify the claim to secure its reimbursement. For this, they first review the denied claim, identify the denial’s root cause, and categorize the denial based on that root cause. Then, they prepare an appeal and submit it along with the corrected claim. Once that’s done, they adjust the billing strategy to avoid such denials in the future.
A/R Follow-Up
This step involves the RCM team tracking and requesting outstanding payments from the payers and patients. To get it done, they analyze and prioritize the aged accounts for follow-ups. Then, they engage with the payers and patients, requesting them to pay the dues. Patients, in particular, are sent patient statements with details of services rendered and their costs.
Patient Payment Collections
During this step, the RCM team works to get the patients to pay their part of the bill. It involves educating those patients about their responsibility. It also includes providing them with flexible payment options to ensure timely payments.
Revenue Analysis And Reporting
This step is more about checking the overall financial performance of a healthcare facility. It involves examining the financial data in a more objective manner. The main aspects of this step include:
- Regular reporting
- Tracking important KPIs
- Setting performance benchmarks
- Ensuring data integrity
- Encouraging collaboration between revenue and financial teams
Compliance
The final and equally important step of RCM is compliance. It is a strategy to ensure proper adherence to regulatory and insurance guidelines. It also involves setting up internal policies and operations to ensure everything remains streamlined. And finally, it involves regular audits to identify lags and apply fixes accordingly.
What is the Goal of RCM?
The process of healthcare RCM mainly helps manage the processes, i.e., the patients’ first interactions, their final payment, and everything in between. It is not just the pathway of healthcare practices getting paid. It involves comprehensive information collection, documentation, and compliance to legal and insurance policies.
More precisely, the revenue cycle is a complex financial process that consists of multiple detailed steps. Mismanagement at any of these steps can lead to claim denials and other issues that can affect your practice’s reputation and bottom-line. RCM helps streamline all these processes to ensure that your healthcare practice enjoys a seamless cash flow while staying adherent to regulatory and insurance guidelines.
Best Practices for RCM Billing Services
Managing an effective revenue cycle requires vigilance across many moving parts. Below are the best practices for effective revenue cycle management:
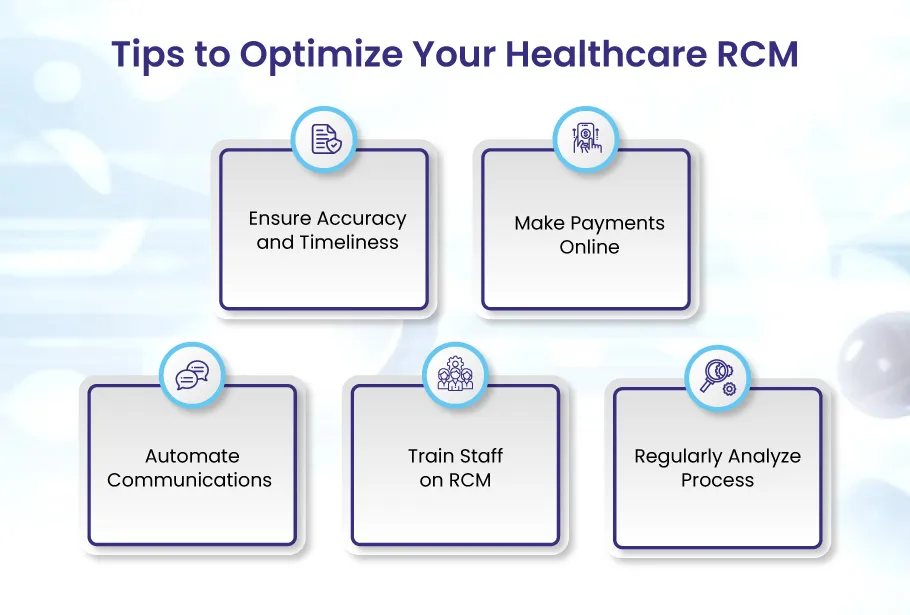
- Conduct regular revenue cycle audits. Identify underperformance to boost claim, denial, and A/R KPIs.
- Verify insurance eligibility upfront. Confirm active coverage and patient responsibility before service delivery to prevent claim rejections.
- Ensure compliant coding and billing. Stay current on coding and payer rules to avoid claim denials for noncompliance.
- Monitor aging claims regularly. Regular reports aid in prioritizing and tracking claims nearing filing deadlines.
- Appeal denied claims quickly. Don’t leave money on the table by letting denial periods expire. Swiftly appeal improper denials.
- Collect patient balances early. Set payment expectations upfront to avoid bad debt.
- Adopt RCM technologies. Use tools like practice management software, automated eligibility checks, claim scrubbing, and analytics.
- Provide ongoing staff education. Regular training ensures personnel are up to date on evolving regulations and best practices.
- Analyze revenue cycle KPIs. Metrics like denial rate, acceptance rate, collection rate, & A/R days reveal opportunities.
- Work rejected claims at the root cause. Don’t rework denied claims without addressing the underlying issue first.
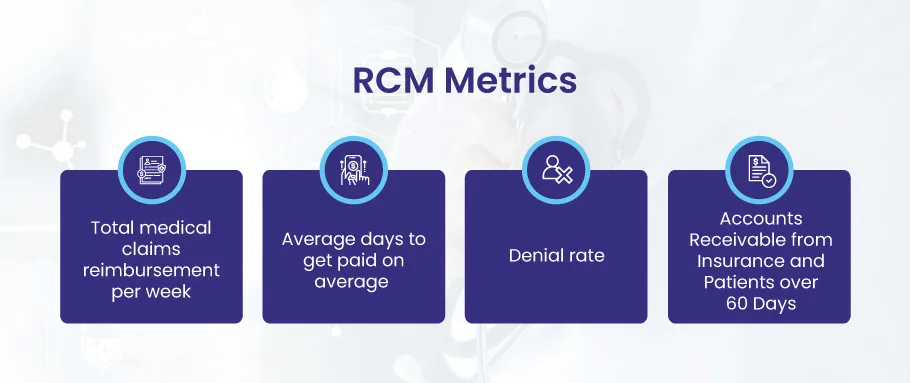
RCM Metrics
- Total medical claims reimbursement per week
- Average days to get paid on average
- Denial rate, and
- Accounts Receivable from Insurance and Patients over 60 Days